Instruments of the orchestra
The symphony orchestra is a large and diverse ensemble that brings together musicians playing a wide variety of instruments - strings, woodwinds, brass, and percussion. The orchestra typically performs 'classical' music, although it can also perform film scores, contemporary compositions, and other genres. Understanding the different instrument families and their layout within the orchestra helps us to appreciate the complexity and beauty of orchestral music.
Instrument Families
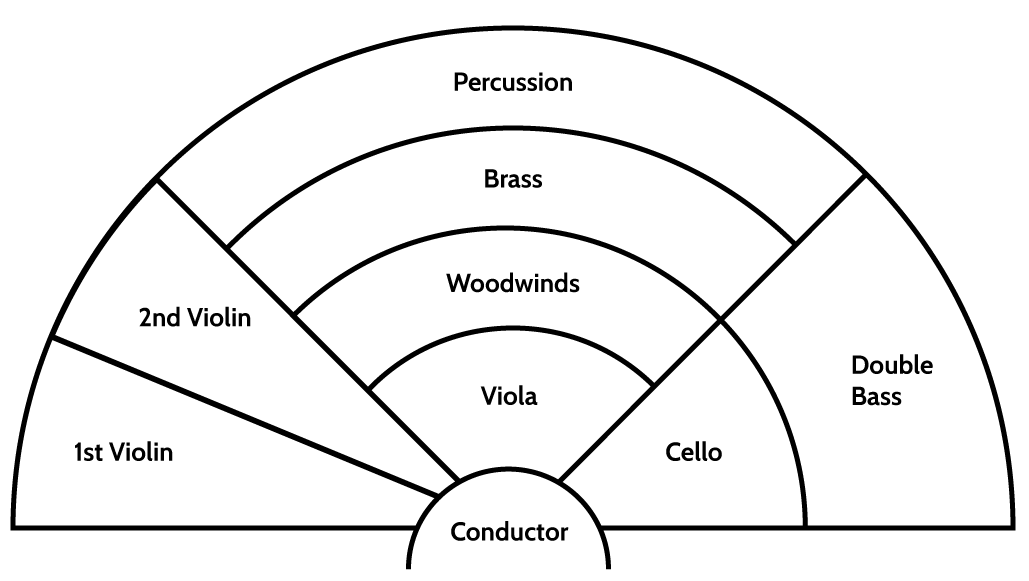
Orchestra Layout
The layout of the orchestra is designed to balance the sound and ensure that all instruments can be heard clearly. This arrangement can vary depending on the size of the orchestra, the conductor's preferences, and the specific requirements of the performance.
Strings: Positioned in the front of the orchestra. The first and second violins are typically on the left side, followed by the violas, cellos, and double basses, which are often on the right side. The harp is usually placed to the side of the strings, near the percussion.
Woodwinds: Positioned behind the strings, often in two rows. Flutes are typically near the front with the oboes to one side. The clarinets and bassoons are commonly in a row behind the flutes and oboes.
Brass: Positioned further back in the orchestra. Trumpets are often placed in the center or slightly to the right, with French horns to the left, trombones and the tuba to the right.
Percussion: Positioned at the back of the orchestra, sometimes to the sides. This section includes instruments like timpani, snare drum, bass drum, cymbals, and xylophone.
